Can Too Much Salt Intake Trigger Eczema Flare-ups?

A healthy diet doesn’t just benefit your overall well-being. It also plays a major role in maintaining healthy skin.
Eating leafy greens and fruits regularly helps the skin appear brighter, more hydrated, and more youthful, thanks to the vitamins and antioxidants they provide.
However, not all nutrients in food have positive effects. One example is salt (sodium).
While the body needs sodium to regulate fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction, excessive intake can harm both general health and skin health.
Too much salt can lead to dehydration, swelling (oedema), and inflammation, making the skin look dull and accelerating the appearance of visible signs of ageing.
In addition, a high-sodium diet may worsen certain skin conditions, such as eczema or atopic dermatitis.
A 2024 study published in JAMA Dermatology involving more than 216,000 participants found a link between high sodium intake and an increased risk of atopic dermatitis—a skin condition characterized by dryness, itching, and rashes.
The study also revealed that higher sodium levels were associated with more severe symptoms in people with this condition.
Effects of excess salt intake on the skin
Too much sodium can have both direct and indirect effects on your skin. Here are several consequences to watch for
1. Triggers skin inflammation
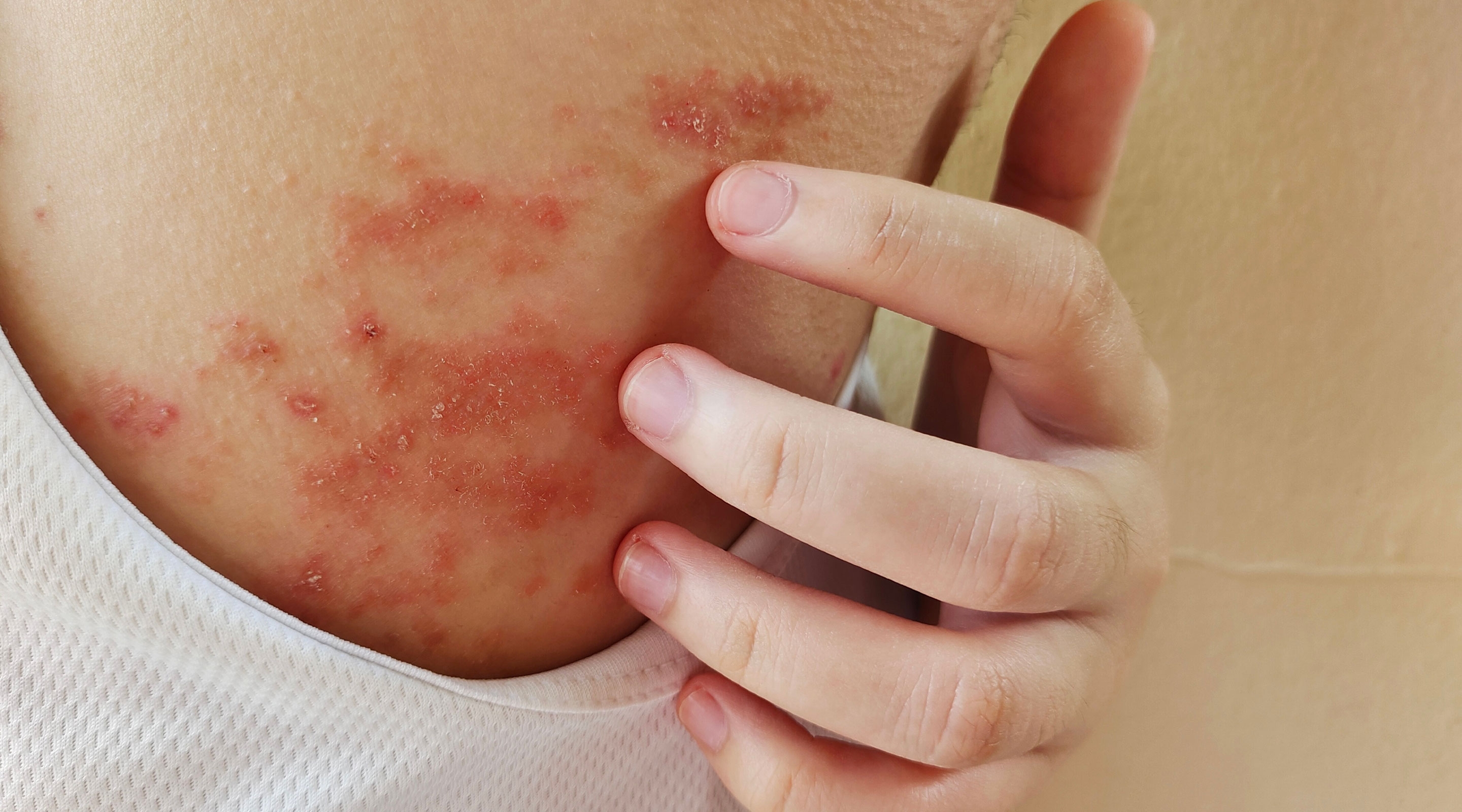
Excess salt can worsen existing skin conditions such as psoriasis and rosacea. Sodium has an inflammatory effect that can cause chronic skin flare-ups.
For people with psoriasis, thick, scaly, red patches may worsen due to fluid retention and increased inflammation.
Similarly, individuals with rosacea may notice more redness, warmth, and visible blood vessels on their skin.
2. Causes dehydration and dry skin
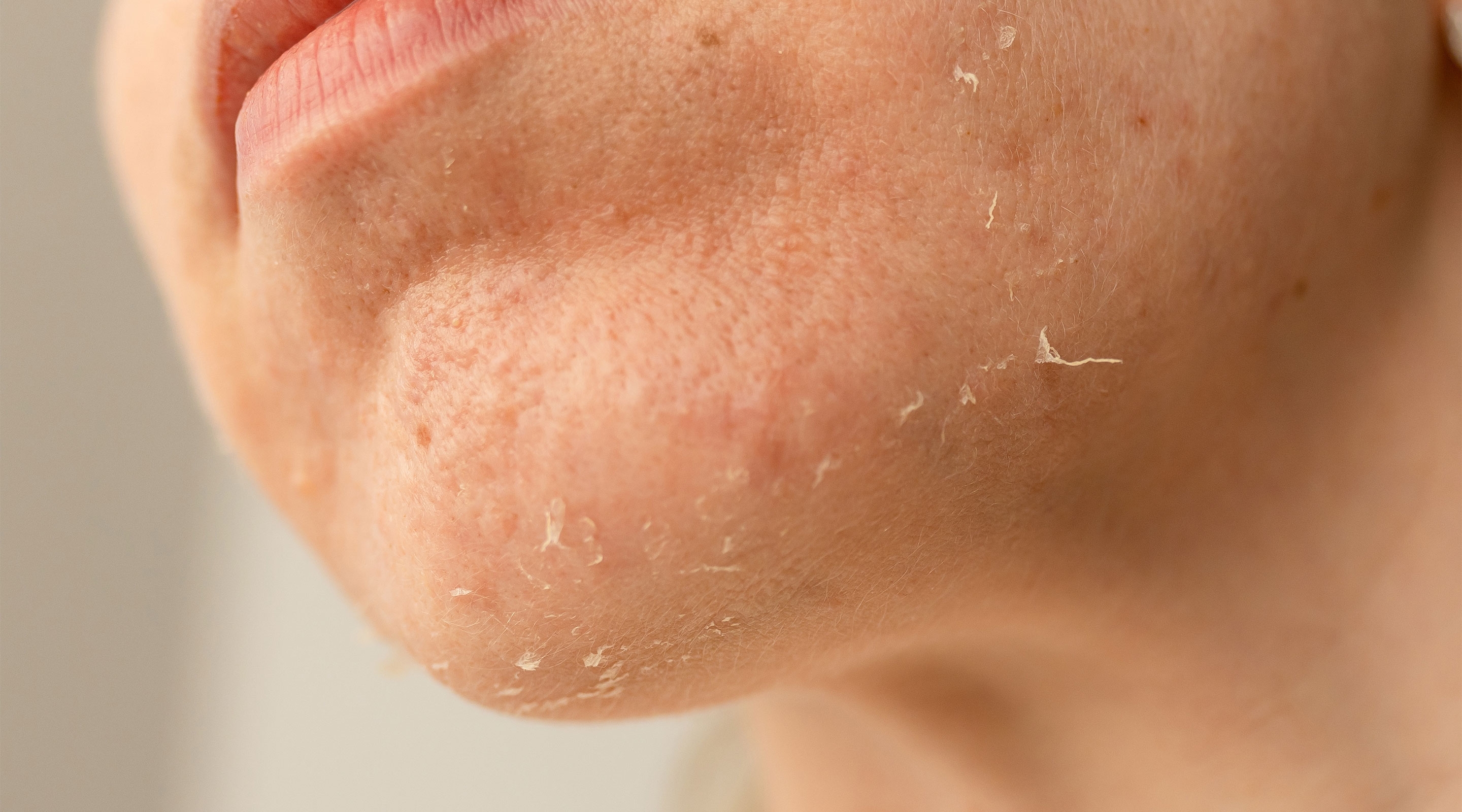
High sodium intake draws water out of the body’s cells to balance salt levels in the blood, leading to dry, rough, and irritated skin.
Dehydrated skin loses its natural protective barrier against pollution and UV rays, making it more prone to irritation and premature aging.
If your skin feels tight, dry, or flaky, it might be a sign that you’re consuming too much salt.
3. Leads to puffiness and swelling
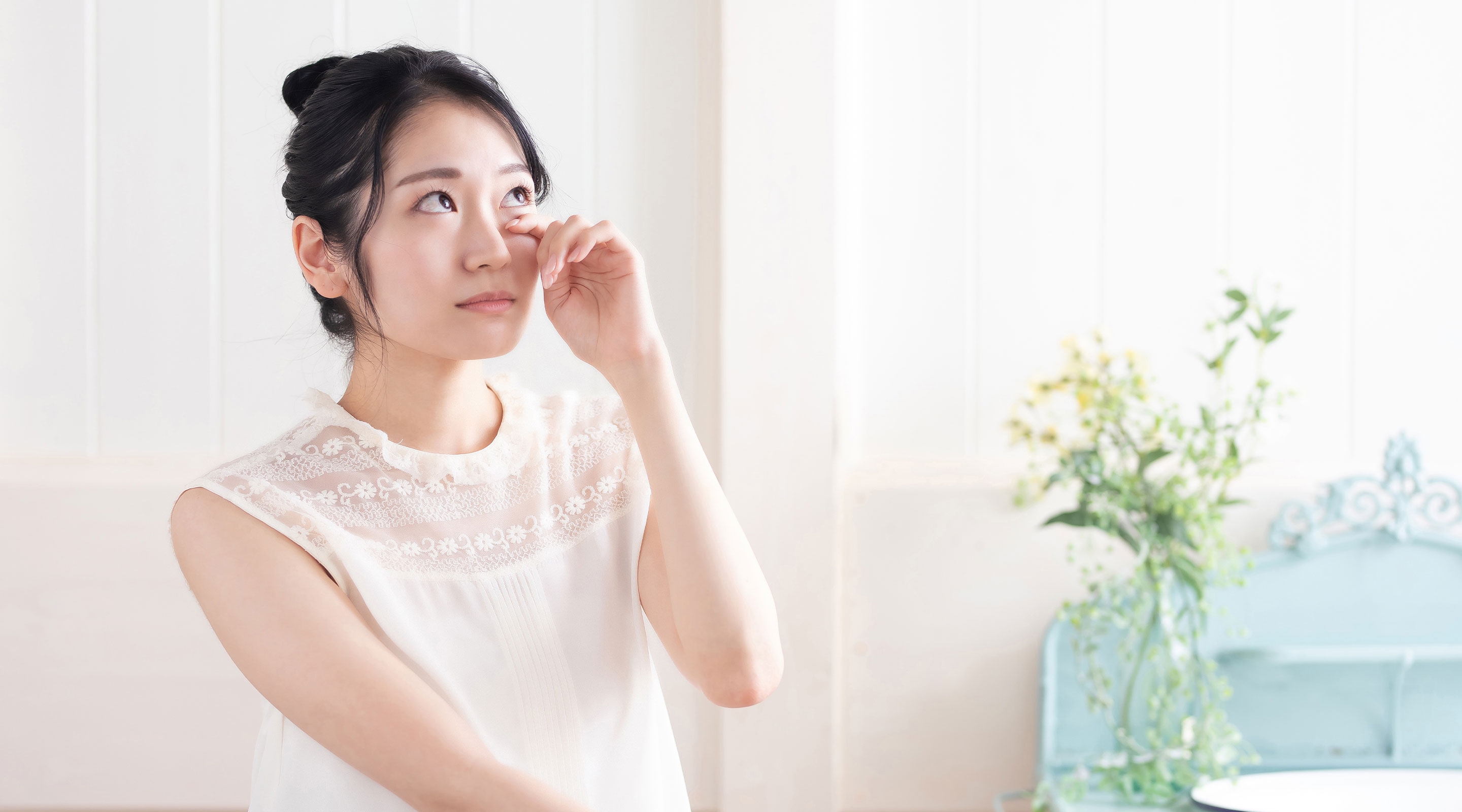

Too much salt causes the body to retain water, leading to puffiness in the face—especially around the eyes—as well as swelling in the hands or feet.
This not only affects your appearance but can also indicate long-term fluid retention, which contributes to high blood pressure and other health risks.
4. Accelerates skin aging
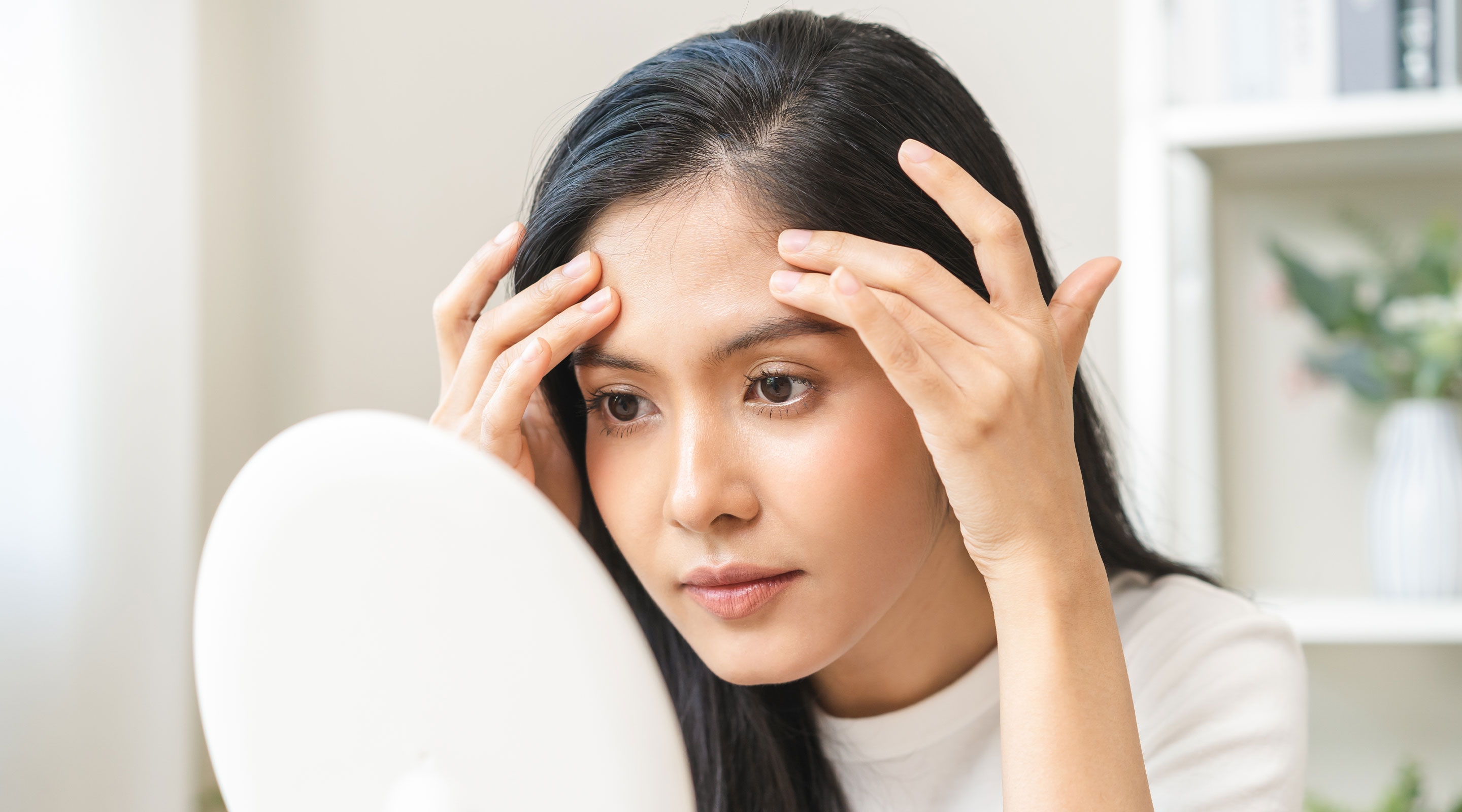

Excess salt contributes to oxidative stress, a condition where free radicals outnumber antioxidants in the body. This damages skin cells and accelerates aging, causing wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Too much salt can also interfere with collagen production—the protein responsible for maintaining skin firmness and elasticity.
As a result, the skin may appear dull, less elastic, and age faster.
How to counter the negative effects of salt on skin

Excess sodium doesn’t just affect blood pressure. It can also harm your skin. Here are some effective ways to protect your skin and balance your salt intake:
1. Control sodium consumption
The Indonesian Ministry of Health recommends limiting sodium intake to no more than 2,000 mg per day, about 5 grams or 1 teaspoon of salt.
Reduce consumption of processed foods, fast foods, and salty snacks, as these are often the main sources of excess sodium.
2. Stay hydrated
High salt intake depletes body fluids, so drinking plenty of water is key to keeping the skin hydrated.
Water helps flush out excess sodium through urine and sweat while maintaining healthy, hydrated skin cells.
Fruits high in water like watermelon, oranges, and cucumbers can also boost hydration naturally.
3. Use hydrating skincare products
Opt for skincare products rich in hydrating ingredients such as hyaluronic acid, glycerin, or ceramides.
These ingredients help attract and retain moisture, strengthen the skin barrier, and prevent dryness caused by excess salt.
For sensitive skin, choose fragrance-free and alcohol-free formulas to avoid irritation.
4. Eat foods rich in potassium
Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body and reduces water retention that causes puffiness.
Include potassium-rich foods like bananas, spinach, avocados, and sweet potatoes in your diet.
These foods also contain antioxidants that support cell regeneration and maintain skin elasticity.
While the body needs small amounts of salt for normal function, excessive sodium intake can worsen skin conditions—leading to dehydration, inflammation, breakouts, and premature aging.
By limiting salt intake, staying hydrated, and maintaining a proper skincare routine, you can keep your skin healthy, supple, and glowing from within.



